
Browsing Toxins By Category
Displaying toxin 1051 - 1075 of 3678 in total
| T3DB ID | Name CAS Number | Formula Weight | Structure | Type | Mechanism of Toxicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T3D0371 | Cadmium chloride 10108-64-2 | CdCl2 183.317 g/mol | 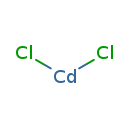 |
| Cadmium initially binds to metallothionein and is transported to the kidney. Toxic effects are observed once the concentration of cadmium exceeds that of available met...more Number of Targets: 22 |
| T3D0720 | Zinc acetate 557-34-6 | C4H6O4Zn 183.497 g/mol | 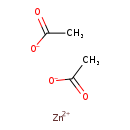 |
| Anaemia results from the excessive absorption of zinc suppressing copper and iron absorption, most likely through competitive binding of intestinal mucosal cells. Unba...more Number of Targets: 1 |
| T3D3959 | Tungsten 7440-33-7 | W 183.840 g/mol | 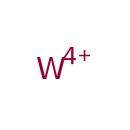 |
| Tungsten oxide (or tungsten trioxide: WO3) is a chemical compound containing oxygen and the transition metal tungsten. Possible health impact of WO3 nanoparticles (NPs...more Number of Targets: 0 |
| T3D1647 | Sodium orthovanadate 13721-39-6 | Na3O4V 183.908 g/mol | 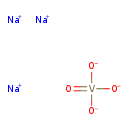 |
| Vanadium damages alveolar macrophages by decreasing the macrophage membrane integrity, thus impairing the cells' phagocytotic ability and viability. The pentavalent fo...more Number of Targets: 47 |
| T3D0087 | 2,4-Dinitrophenol 51-28-5 | C6H4N2O5 184.106 g/mol | 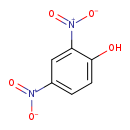 |
| Acute 2,4-dinitrophenol poisoning (from ingestion) involves uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation, which presumably reduces body's reservoirs of high-energy phosphat...more Number of Targets: 1 |
| T3D1739 | Magnesium bromide 7789-48-2 | Br2Mg 184.113 g/mol | 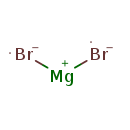 |
| Bromine is a powerful oxidizing agent and is able to release oxygen free radicals from the water in mucous membranes. These free radicals are also potent oxidizers and...more Number of Targets: 6 |
| T3D0026 | Benzidine 92-87-5 | C12H12N2 184.237 g/mol | 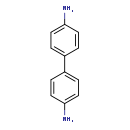 |
| N-acetylated benzidine metabolites are believed to form adducts with nucleic acids. Carcinogenesis is initiated when they are activated by peroxidation by prostaglandi...more Number of Targets: 13 |
| T3D0167 | 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine 122-66-7 | C12H12N2 184.237 g/mol | 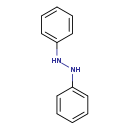 |
| Two of the known metabolites, aniline and benzidine, may contribute to the toxicity and/or carcinogenicity of 1,2-diphenylhydrazine. Nonneoplastic liver lesions, hepat...more Number of Targets: 3 |
| T3D4847 | Undecylenic acid 112-38-9 | C11H20O2 184.275 g/mol | 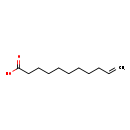 |
| Not Available Number of Targets: 1 |
| T3D2717 | Enflurane 13838-16-9 | C3H2ClF5O 184.492 g/mol | 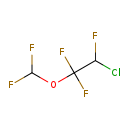 |
| Enflurane induces a reduction in junctional conductance by decreasing gap junction channel opening times and increasing gap junction channel closing times. Enflurane a...more Number of Targets: 12 |
| T3D2882 | Isoflurane 26675-46-7 | C3H2ClF5O 184.492 g/mol | 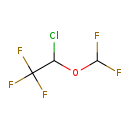 |
| Isoflurane induces a reduction in junctional conductance by decreasing gap junction channel opening times and increasing gap junction channel closing times. Isoflurane...more Number of Targets: 9 |
| T3D1807 | o-Xylyl bromide 89-92-9 | C8H9Br 185.061 g/mol |  |
| Organobromide compounds such as o-Xylyl bromide are strong alkylating agents. Consequently they can readily modify free thiols (cysteines) and methionine residues of ...more Number of Targets: 1 |
| T3D1808 | p-Xylyl bromide 28258-59-5 | C8H9Br 185.061 g/mol |  |
| Organobromide compounds such as p-Xylyl bromide are strong alkylating agents. Consequently they can readily modify free thiols (cysteines) and methionine residues of ...more Number of Targets: 1 |
| T3D1809 | m-Xylyl bromide 620-13-3 | C8H9Br 185.061 g/mol |  |
| Organobromide compounds such as m-Xylyl bromide are strong alkylating agents. Consequently they can readily modify free thiols (cysteines) and methionine residues of ...more Number of Targets: 1 |
| T3D0910 | 4-Chlorophenyl-N-methylcarbamate 2620-53-3 | C8H8ClNO2 185.608 g/mol | 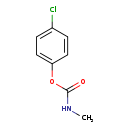 |
| 4-Chlorophenyl-N-methylcarbamate is a cholinesterase or acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor. Carbamates form unstable complexes with chlolinesterases by carbamoylati...more Number of Targets: 2 |
| T3D0308 | Methylarsonic acid, disodium salt 19444-53-2 | CH5AsNa2O3 185.949 g/mol | 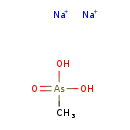 |
| Arsenic and its metabolites disrupt ATP production through several mechanisms. At the level of the citric acid cycle, arsenic inhibits pyruvate dehydrogenase and by co...more Number of Targets: 44 |
| T3D0815 | Angelicin 523-50-2 | C11H6O3 186.164 g/mol | 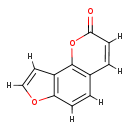 |
| The mechanism of action many furocoumarins is based on their ability to form photoadducts with DNA and other cellular components such as RNA, proteins, and several pro...more Number of Targets: 4 |
| T3D0825 | Psoralen 66-97-7 | C11H6O3 186.164 g/mol | 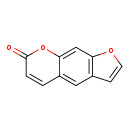 |
| The mechanism of action many furocoumarins is based on their ability to form photoadducts with DNA and other cellular components such as RNA, proteins, and several pro...more Number of Targets: 4 |
| T3D4907 | 4,5-Dichloro-3H-1,3-dithiol-2-one 1192-52-5 | C3Cl2OS2 187.068 g/mol | 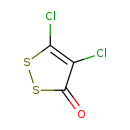 |
| Not Available Number of Targets: 2 |
| T3D2965 | Selegiline 14611-51-9 | C13H17N 187.281 g/mol |  |
| Although the mechanisms for selegiline's beneficial action in the treatment of Parkinson's disease are not fully understood, the selective, irreversible inhibition of ...more Number of Targets: 4 |
| T3D0988 | Molinate 2212-67-1 | C9H17NOS 187.302 g/mol | 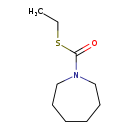 |
| Some thiocarbamates (EPTC, Molinate, Pebulate, and Cycloate) share a common mechanism of toxicity, i.e. the inhibition of acetylcholinesterase. An acetylcholinesterase...more Number of Targets: 7 |
| T3D0713 | Zinc chromate 13530-65-9 | CrH6O4Zn 187.450 g/mol |  |
| Anaemia results from the excessive absorption of zinc suppressing copper and iron absorption, most likely through competitive binding of intestinal mucosal cells. Unba...more Number of Targets: 6 |
| T3D0286 | Copper(II) arsenite 10290-12-7 | AsCuHO3 187.474 g/mol | 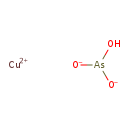 |
| Excess copper is sequestered within hepatocyte lysosomes, where it is complexed with metallothionein. Copper hepatotoxicity is believed to occur when the lysosomes bec...more Number of Targets: 49 |
| T3D1212 | Copper(II) nitrate 3251-23-8 | CuN2O6 187.556 g/mol | 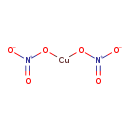 |
| Excess copper is sequestered within hepatocyte lysosomes, where it is complexed with metallothionein. Copper hepatotoxicity is believed to occur when the lysosomes bec...more Number of Targets: 15 |
| T3D1753 | Silver bromide 7785-23-1 | AgBr 187.772 g/mol | 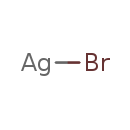 |
| Bromine is a powerful oxidizing agent and is able to release oxygen free radicals from the water in mucous membranes. These free radicals are also potent oxidizers and...more Number of Targets: 23 |