
Browsing Toxins By Category
Displaying toxin 1551 - 1575 of 3678 in total
| T3DB ID | Name CAS Number | Formula Weight | Structure | Type | Mechanism of Toxicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T3D2893 | Halazepam 23092-17-3 | C17H12ClF3N2O 352.738 g/mol | 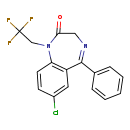 |
| Benzodiazepines bind nonspecifically to benzodiazepine receptors BNZ1, which mediates sleep, and BNZ2, which affects affects muscle relaxation, anticonvulsant activity...more Number of Targets: 18 |
| T3D2453 | Gyromitrin 16568-02-8 | C4H8N2O 100.119 g/mol | 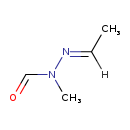 |
| The toxicity is caused by the conversion of the hydrazine (gyromitrin) to a hydrazine metabolite intermediate monomethylhydrazine. This occurs when gyromitrin begins t...more Number of Targets: 0 |
| T3D4051 | Gymnodimine 173792-58-0 | C32H45NO4 507.704 g/mol | 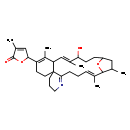 |
| Gymnodimine exerts its toxic effects via binding to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors with picomolar affinities with no sign of apparent reversibility in short time fr...more Number of Targets: 0 |
| T3D0135 | Guthion 86-50-0 | C10H12N3O3PS2 317.324 g/mol | 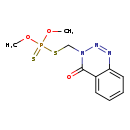 |
| Guthion is a cholinesterase or acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor. A cholinesterase inhibitor (or 'anticholinesterase') suppresses the action of acetylcholinesteras...more Number of Targets: 14 |
| T3D4149 | Guanidoacetic acid 352-97-6 | C3H7N3O2 117.107 g/mol | 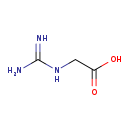 |
| Uremic toxins such as guanidinoacetic acid are actively transported into the kidneys via organic ion transporters (especially OAT3). Increased levels of uremic toxins ...more Number of Targets: 6 |
| T3D4174 | Guanidinosuccinic acid 6133-30-8 | C5H9N3O4 175.143 g/mol | 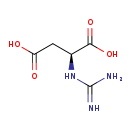 |
| Uremic toxins such as guanidinosuccinic acid are actively transported into the kidneys via organic ion transporters (especially OAT3). Increased levels of uremic toxin...more Number of Targets: 3 |
| T3D3561 | Guanidine nitrate 506-93-4 | CH6N4O3 122.083 g/mol | 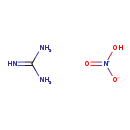 |
| Nitrate's toxicity is a result of it's conversion to nitrite once in the body. Nitrite causes the autocatalytic oxidation of oxyhemoglobin to hydrogen peroxide and met...more Number of Targets: 9 |
| T3D4172 | Guanidine 113-00-8 | CH5N3 59.071 g/mol | 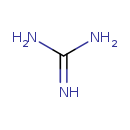 |
| Uremic toxins such as guaniidine are actively transported into the kidneys via organic ion transporters (especially OAT3). Increased levels of uremic toxins can stimul...more Number of Targets: 8 |
| T3D4556 | Guaifenesin 93-14-1 | C10H14O4 198.216 g/mol | 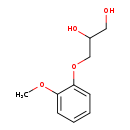 |
| Guaifenesin may act as an irritant to gastric vagal receptors, and recruit efferent parasympathetic reflexes that cause glandular exocytosis of a less viscous mucus mi...more Number of Targets: 0 |
| T3D4576 | Guaiacol 1990-05-01 | C7H8O2 124.137 g/mol | 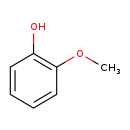 |
| Not Available Number of Targets: 1 |
| T3D4696 | Griseofulvin 126-07-8 | C17H17ClO6 352.766 g/mol | 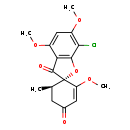 |
| Griseofulvin is fungistatic, however the exact mechanism by which it inhibits the growth of dermatophytes is not clear. It is thought to inhibit fungal cell mitosis an...more Number of Targets: 1 |
| T3D3092 | Grayanotoxin III 4678-45-9 | C20H34O6 370.480 g/mol |  |
| Grayanotoxins bind to specific sodium ion channels in cell membranes. The grayanotoxins prevent inactivation, leaving excitable cells depolarized. (L1251) Number of Targets: 14 |
| T3D3091 | Grayanotoxin II 4678-44-8 | C20H32O5 352.465 g/mol | 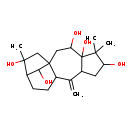 |
| Grayanotoxins bind to specific sodium ion channels in cell membranes. The grayanotoxins prevent inactivation, leaving excitable cells depolarized. (L1251) Number of Targets: 14 |
| T3D3090 | Grayanotoxin I 4720-09-6 | C22H36O7 412.517 g/mol |  |
| Grayanotoxins bind to specific sodium ion channels in cell membranes. The grayanotoxins prevent inactivation, leaving excitable cells depolarized. (L1251) Number of Targets: 14 |
| T3D2498 | Grammotoxin 152617-90-8 | Not Available 9600.980 g/mol |  |
| Grammotoxin inhibits P-, Q- and N-type voltage-gated calcium channels in neurons. Binding to the calcium channels modifies their voltage-dependent gating. This makes i...more Number of Targets: 3 |
| T3D4039 | Gonyautoxin II 60508-89-6 | C10H17N7O8S 395.349 g/mol |  |
| The gonyautoxin toxicity is caused by the reversibly binding to its receptor site on the voltage-gated sodium channel on excitable cells, thus blocking the influx of N...more Number of Targets: 0 |
| T3D4038 | Gonyautoxin I 60748-39-2 | C10H17N7O9S 411.348 g/mol |  |
| The gonyautoxin toxicity is caused by the reversibly binding to its receptor site on the voltage-gated sodium channel on excitable cells, thus blocking the influx of N...more Number of Targets: 0 |
| T3D1731 | Gold(III) bromide 10294-28-7 | AuBr3 436.679 g/mol |  |
| Bromine is a powerful oxidizing agent and is able to release oxygen free radicals from the water in mucous membranes. These free radicals are also potent oxidizers and...more Number of Targets: 6 |
| T3D4442 | Glyoxylic acid 298-12-4 | C2H2O3 74.036 g/mol | 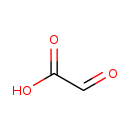 |
| Not Available Number of Targets: 0 |
| T3D4830 | Glycoluril 496-46-8 | C4H6N4O2 142.116 g/mol | 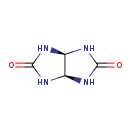 |
| Not Available Number of Targets: 2 |
| T3D3660 | Glycolic acid 79-14-1 | C2H4O3 76.051 g/mol | 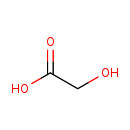 |
| Glycolic acid's toxicity is due to its metabolism to oxalic acid. Glycolic and oxalic acid, along with excess lactic acid, are responsible for the anion gap metabolic ...more Number of Targets: 1 |
| T3D4318 | Glycine 56-40-6 | C2H5NO2 75.067 g/mol | 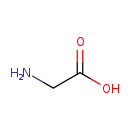 |
| In the CNS, there exist strychnine-sensitive glycine binding sites as well as strychnine-insensitive glycine binding sites. The strychnine-insensitive glycine-binding ...more Number of Targets: 31 |
| T3D4224 | Glycidol 556-52-5 | C3H6O2 74.079 g/mol | 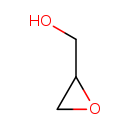 |
| Not Available Number of Targets: 2 |
| T3D4360 | Glycerol 56-81-5 | C3H8O3 92.094 g/mol | 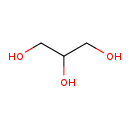 |
| Not Available Number of Targets: 12 |
| T3D4330 | Glyceric acid 473-81-4 | C3H6O4 106.077 g/mol | 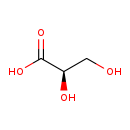 |
| Glyceric acid is a compound that is secreted excessively in the urine by patients suffering from D-glyceric aciduria and D-glycerate anemia. Deficiency of human glycer...more Number of Targets: 1 |